To celebrate the milestone of the 20th volume of the International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, the editorial team assembled a selection of journal papers representing the excellent work from the advanced ceramics community. The focus this month is advanced sintering.
Read MoreHumic substances are beneficial to agriculture, but they can aggravate pollution in water by interacting with disinfectants to produce toxic byproducts. Hydrogarnet has shown excellent potential as an adsorbent for humic substances, and researchers in Japan investigated the effects of heat treatments to control hydrogarnet composition and adsorption properties.
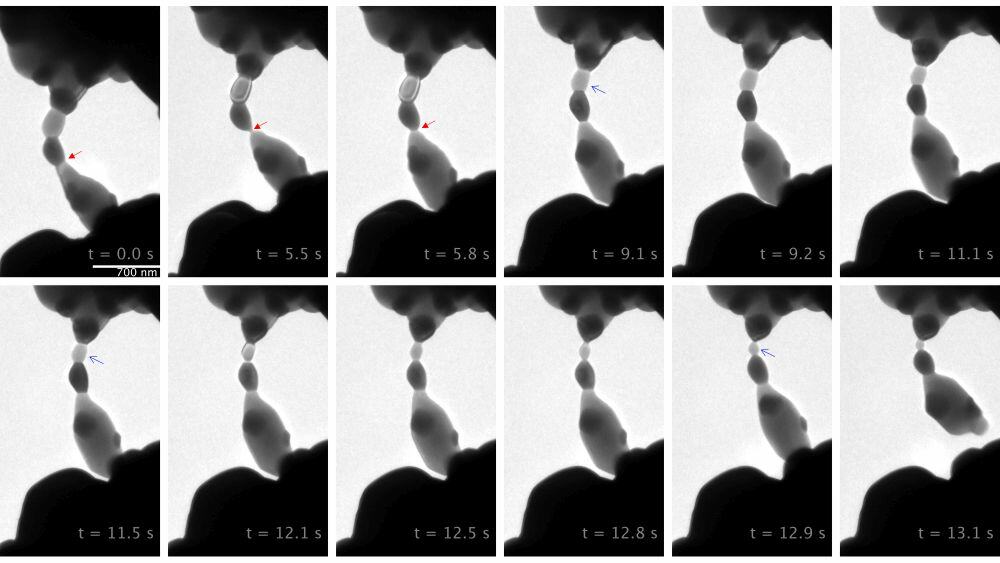
Read MoreUnderstanding the underlying mechanisms of rapid and energy-efficient flash sintering is key to tailoring the materials and processes to meet a wide range of performance requirements. Four recent articles in ACerS journals characterize and quantify some of these atomic-level phenomena.
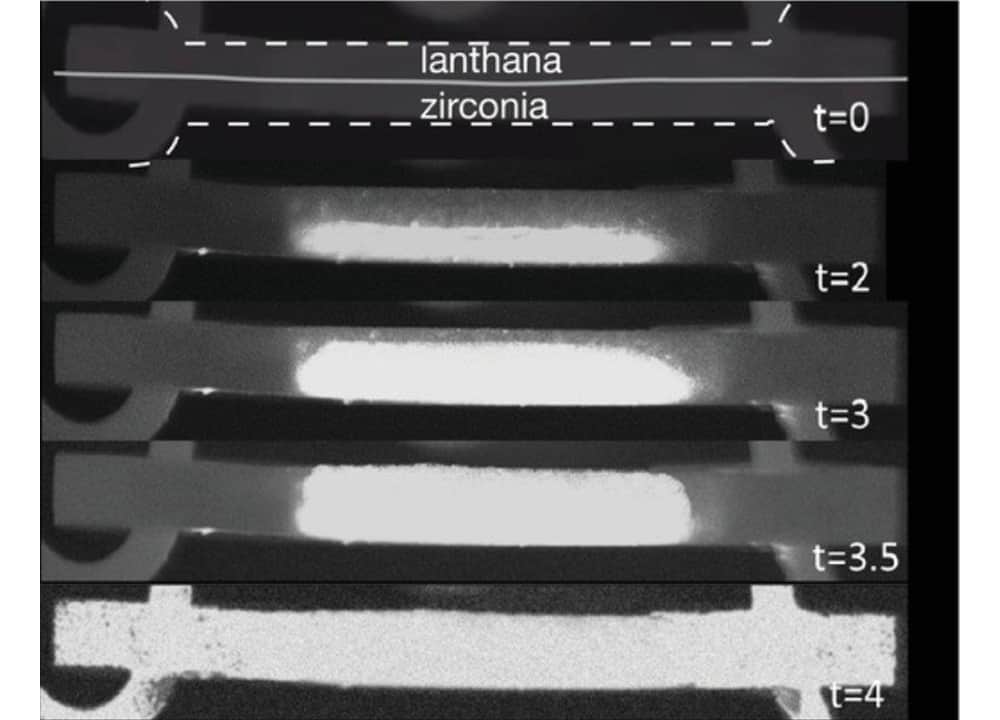
Read MoreChances of local overheating are likely when densifying ceramics through microwave or flash sintering. In a recent paper, researchers in France discuss factors that drive hot spot development and describe possible ways to manage the phenomenon.
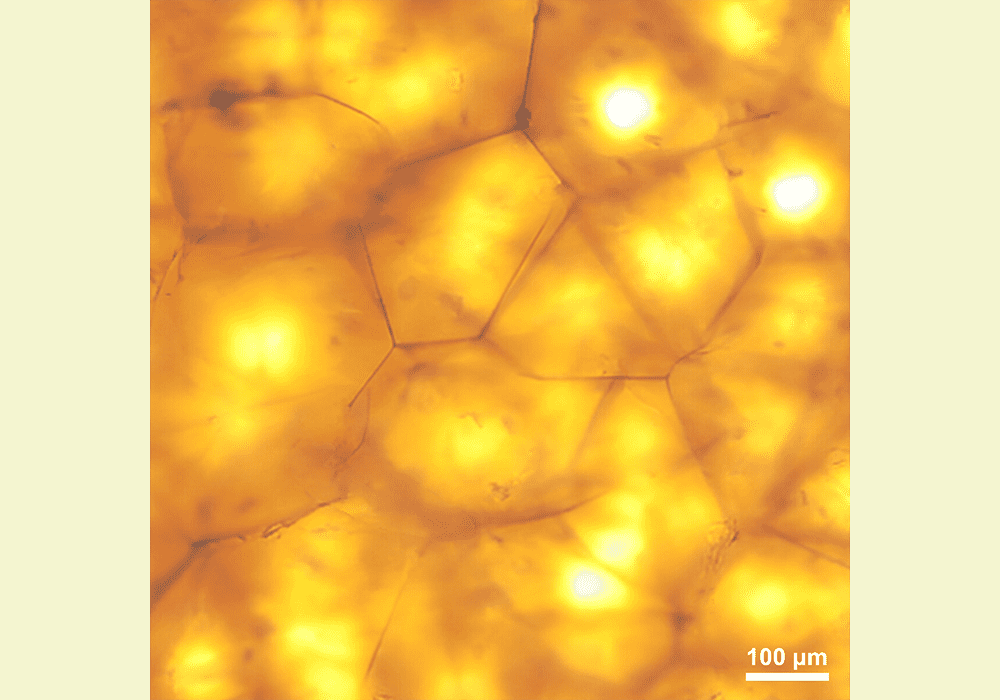
Read MoreProcessing ceramics requires accurate knowledge of their thermal, chemical, and mechanical behaviors. In today’s CTT, ACerS Fellow Shen Dillon shares recent work he and collaborators in China and the United States published on new models for understanding sintering and creep behaviors in ceramics.
Read MoreMolten salt electrochemical conversion may offer an economic and relatively clean way to extract pure carbon products from stored carbon dioxide emissions. In a recently published open-access paper, researchers from the University of Science and Technology Beijing summarize the successes and challenges of this process.
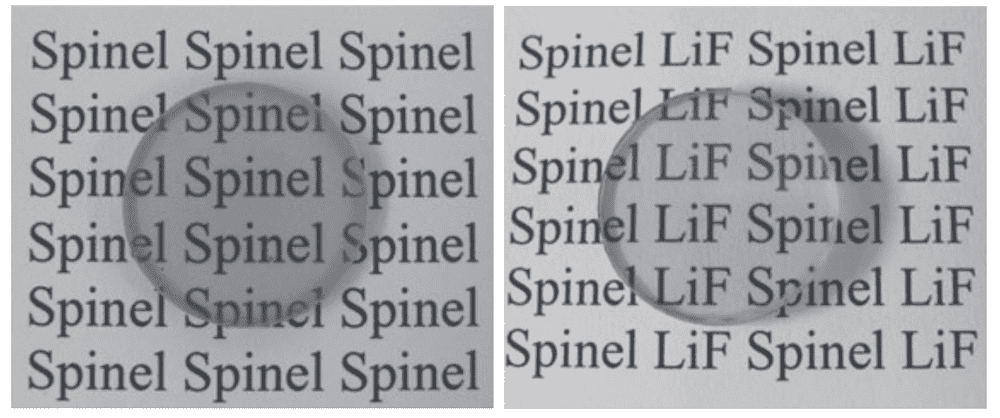
Read MoreCurrent sintering methods used to obtain transparent ceramics face several challenges, including strict processing conditions and limited shape and size control. Researchers led by South China University of Technology presented a new general strategy for constructing dual-phase transparent ceramics from hybridized glasses that offers shape and size control as well as the potential for functionalization.
Read MoreAwareness of lead’s toxicity drives research on alternative lead-free piezoelectric materials. But traditional high-temperature sintering processes can inadvertently deteriorate a lead-free ceramic’s piezoelectric response. A two-step sintering process can minimize this deterioration, and researchers in China identified the optimum temperature and dwell time for the first step.
Read MoreCarbon nano-onions are a newer carbon nanostructure with great potential in application, but synthesizing these materials conventionally requires high temperatures, expensive feedstock, or corrosive environments. Researchers at Nagoya Institute of Technology used a one-step microwave pyrolysis process to turn fish scales into carbon nano-onions with highly crystalline and functionalized structures.
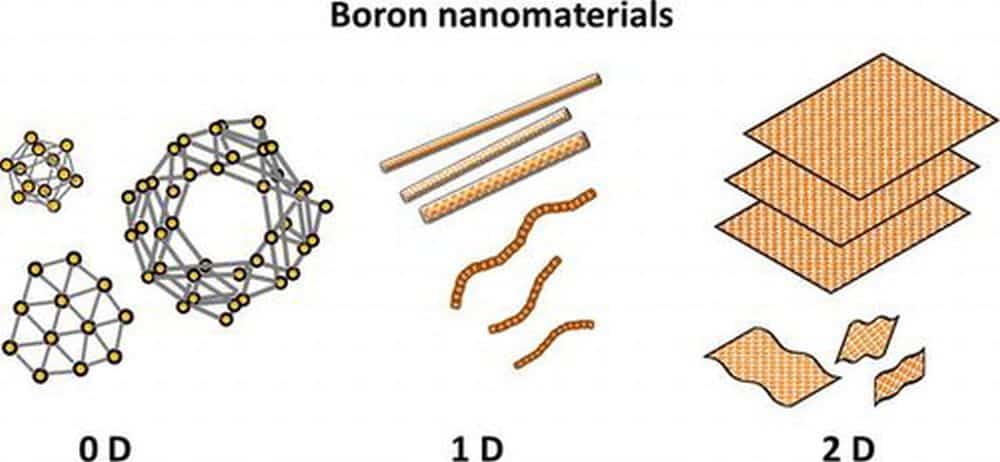
Read MoreIn the past decade, computational research has dominated over experimental studies of boron nanomaterials. A recent open-access paper contributes a new addition to the experimental literature by demonstrating that double-pulse laser ablation can be used to synthesize boron nanorods, nanowires, and nanotubes.
Read More