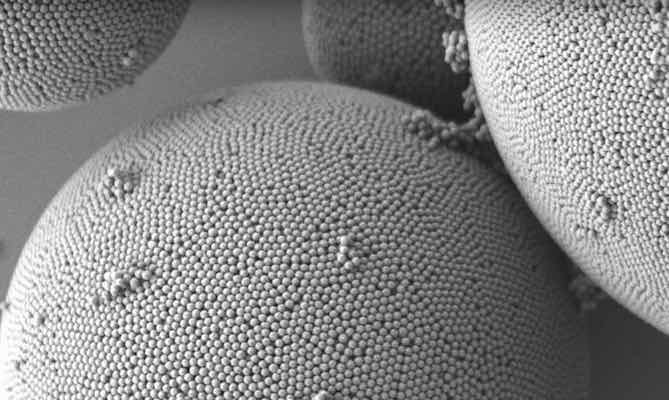
Researchers report a simple method to manufacture biocompatible structural colors using only melanin and silica. The silica shell provides a buffer layer of tunable thickness that allows customization of the particular color, offering the potential to fabricate a new breed of long-lasting pigments that don’t fade.
Read MoreEnvironmental concerns and decreased demand have contributed to the decline of coal as a fuel source. The Oak Ridge National Laboratory is developing value-added products that may eventually revive the coal industry.
Read MoreScientists at the University of California, San Diego have developed a method called water-assisted flash sintering that can densify powders to 98% of theoretical density in just 30 seconds. Their method takes place at room temperature and requires no external heating.
Read MoreResearchers at Jožef Stefan Institute (Ljubljana, Slovenia), the National Institute of Chemistry (Ljubljana, Slovenia), and Stockholm University (Stockholm, Sweden) have developed a new method to rapidly and evenly densify nanoceramics, offering incredible potential to save a lot of time and energy in sintering processes.
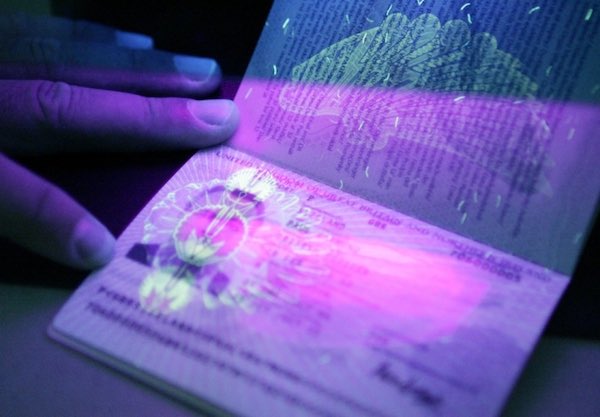
Read MoreScientists at ITMO University in Russia recently developed a scalable method of printing europium-doped zirconia nanoparticles into beautifully glowing security holograms that could secure the authenticity of printed documents and more.
Read MoreAccording to a laboratory compositional analysis, the elemental recipe for a 129-g Apple iPhone includes about 24.1% aluminum, 15.4% carbon, 14.4% iron, and 14.5% oxygen by weight. And altogether, that pile of smartphone powder—ground from a $700 device—has a raw elemental value of about $1.03.
Read MoreThe CEO of advanced materials manufacturing company American Elements recently met with White House officials to vie for the government to nationalize the U.S.’s last remaining rare earth mine.
Read MoreThe August 2017 issue of the ACerS Bulletin—featuring articles about boron carbide for lightweight ceramic armor, an update on German ceramic R&D activities, and where big data meets materials science—is now available online.
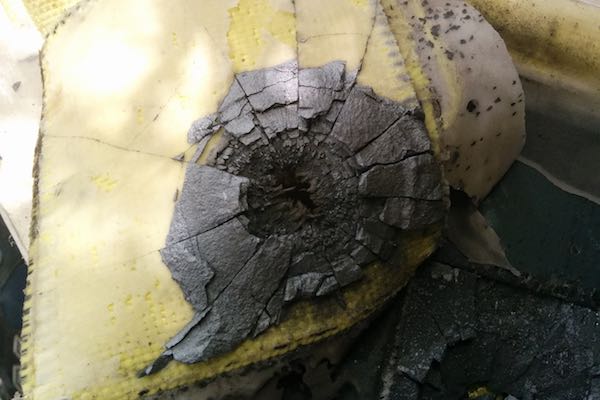
Read MoreIBM scientists report that they have developed a simple technique to peel extremely thin layers of gallium nitride from a bulk wafer of the material—a breakthrough in manufacturing techniques for this expensive material.
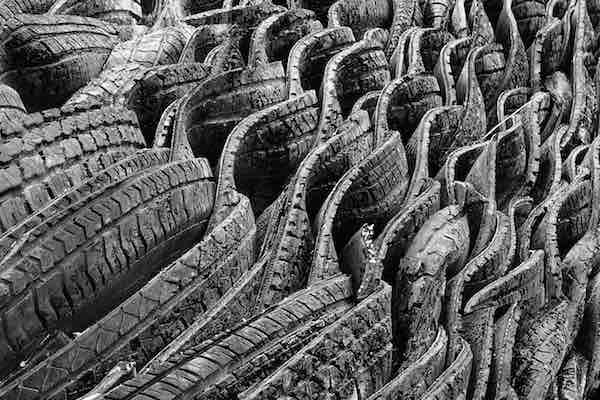
Read MoreScientists at the University of British Colombia (Vancouver, British Colombia, Canada) have a new strategy that just might be going somewhere—they’ve devised a technique to incorporate recycled rubber tire fibers into concrete to reuse the waste material, improve the durability of concrete, and reduced the carbon footprint of the concrete industry.
Read More