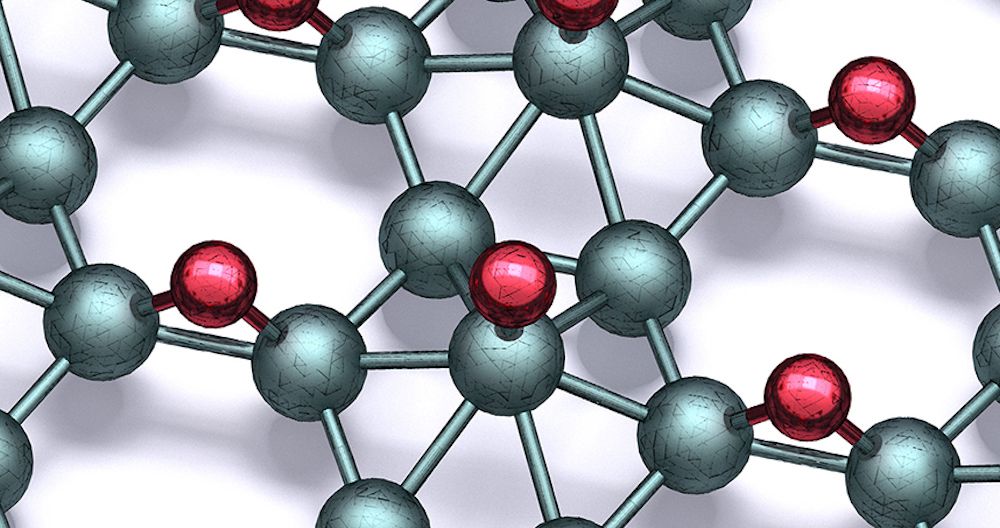
The 2D material borophene holds a lot of potential due to its flexibility, strength, and diverse atomic structure—but rapid oxidation of borophene in air makes application difficult. Researchers led by Northwestern University experimentally investigated the hydrogenation of borophene to see how well it stabilizes the material for practical use.
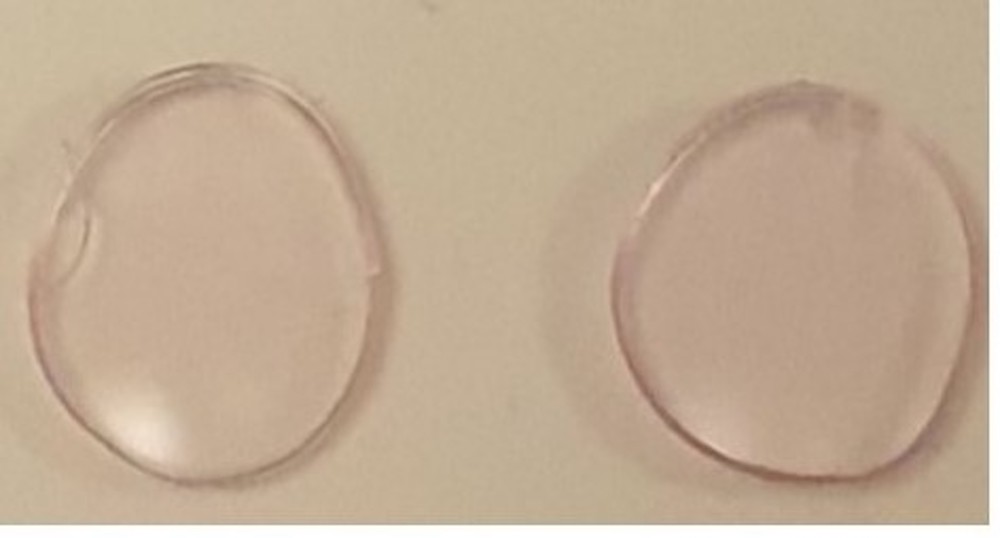
Read MorePeople who have color vision deficiency see colors differently from others. Tinted glasses and contact lenses offer a way to manage the condition, but to date only the former option is reliably effective. Researchers developed a new type of tinted contact lens using gold nanoparticles that shows potential for commercial scale-up.
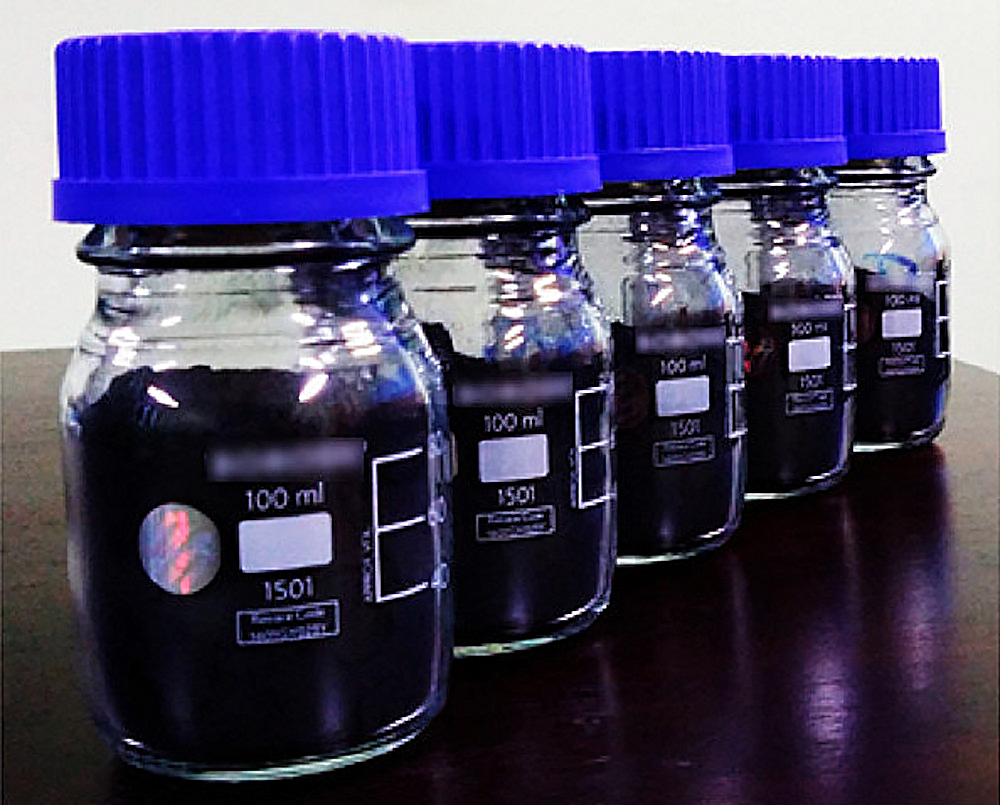
Read MoreCurrent methods of graphene production face tradeoffs among speed, cost, and material quality. Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Patna propose a new method based on plasma spraying that may offer the best outcome for all of these factors.
Read MoreOrganically linked supercrystals are an emerging type of nanocomposite that could prove useful in next-generation electronic devices and as biomimetic structural materials. Researchers led by the Hamburg University of Technology in Germany have conducted several studies on these materials, with the most recent one exploring its deformation mechanisms.
Read MoreGraphene nanoribbons are a family of carbon allotropes that exhibit semiconducting properties promising for electronic applications. However, the conventional bottom-up synthesis method for graphene nanoribbons is a costly and low-yield process. Researchers led by the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology developed an alternative method that is higher yield and lower cost.
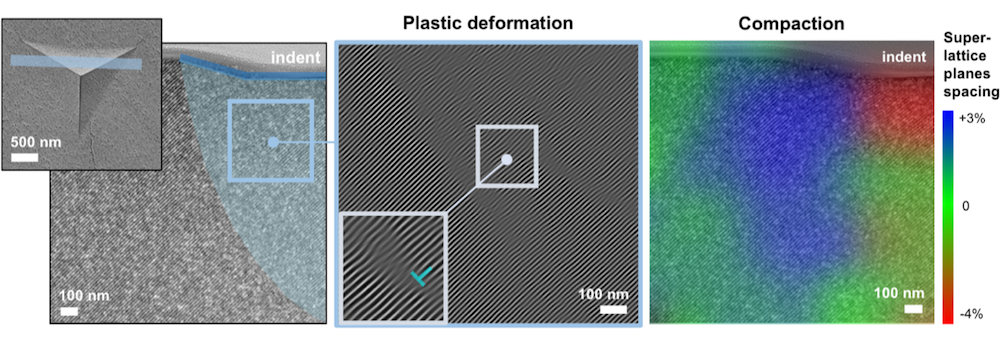
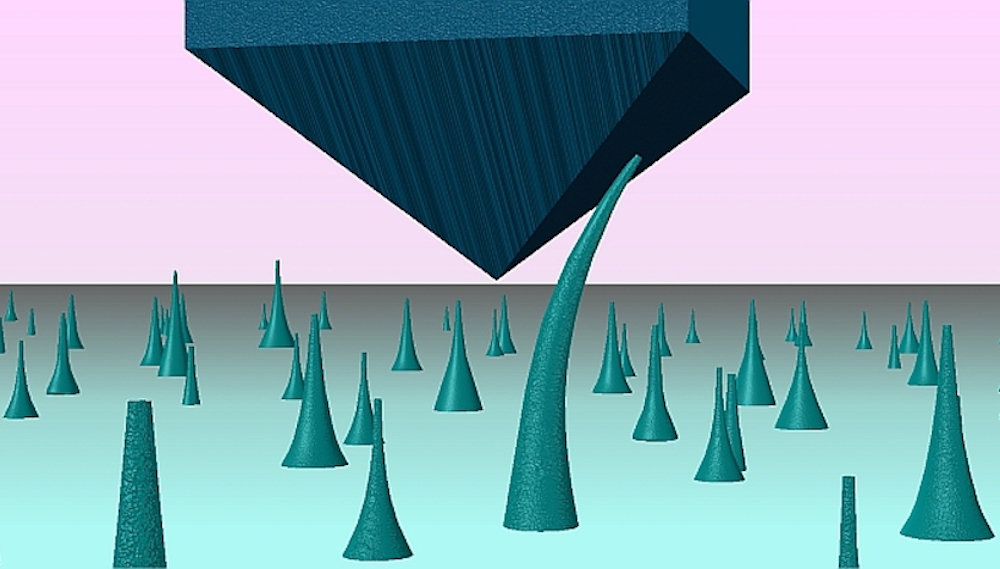
Read MoreDiamonds have many desirable properties for application in electronic devices, but their rigid crystalline structure and brittle nature make it difficult to use diamonds for such a purpose. An international team of researchers led by City University of Hong Kong revealed in 2018 that diamonds are bendable on the nanoscale, and a follow-up paper published by them this month expands on that finding.
Read MoreSurface plasmon polaritons are a type of surface wave that, when harnessed, show potential to improve various processes that take place on the nanoscale, such as molecular imaging. Researchers from two places in Russia propose a new scheme using quantum dots and graphene to more efficiently convert light into surface plasmon polaritons for use in such applications.
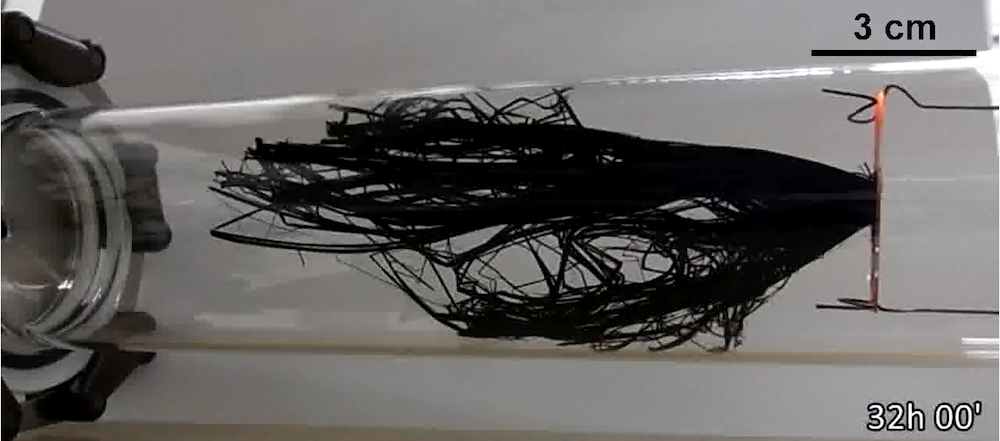
Read MoreCarbon nanotubes demonstrate much higher tensile strength than carbon fibers, but growing nanotubes in bulk while retaining this property is an obstacle that limits their commercial applications. Researchers in Japan developed a new fabrication method that could overcome the challenge of growing nanotubes in bulk.
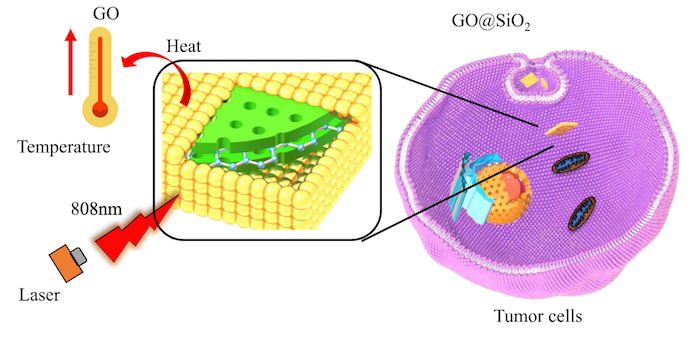
Read MoreTraditional methods of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy for treating cancer can be extremely taxing on the body. Photothermal therapy is a minimally invasive and locally focused alternative, and a recent paper by researchers in China looks at the potential of a new graphene oxide-templated gold nanosheet for use in this treatment.
Read MoreTransparent ceramics serve as the gain medium in many commercial lasers, yet the push to develop new and improved ceramics for this application continues. In two papers published this year, an international team of researchers investigates the influence of different processing parameters on the properties of nanocomposite yttrium magnesium oxide ceramics.
Read More