Agriculture and livestock management has relied largely on antimicrobial drugs to combat plant diseases, but this overreliance contributes to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance. Silver-based nanoparticles could serve as an alternative method to protect plants from pathogens, as discussed in a recent review paper.
Read MoreTheoretical studies have predicted that 2D silicon carbide in a stable honeycomb structure is possible, but experimentally achieving this material has proven difficult. Two recent papers successfully synthesized monolayer silicon carbide using top-down and bottom-up synthesis methods, respectively.
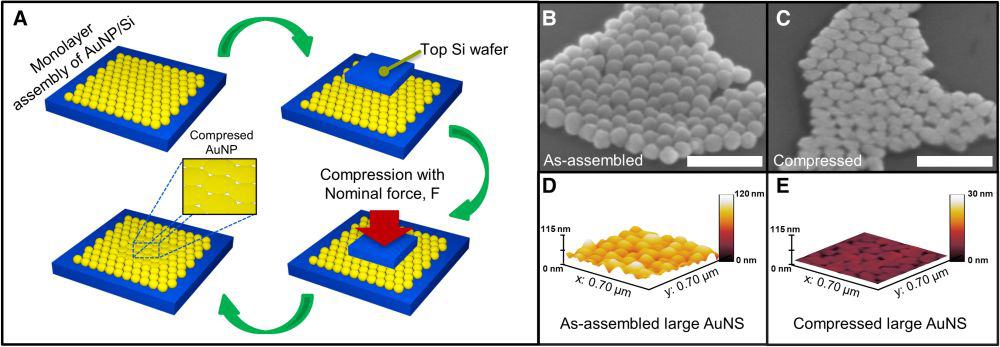
Read MoreTwo-dimensional thin films are often fabricated using bottom-up solution-based techniques, such as electrochemical deposition and atomic layer deposition. Now researchers have reported a top-down, solid-state method based on the age-old Egyptian craft of goldbeating that they say is generalizable to various metallic, polymeric, or ceramic nanoparticles.
Read MoreQuantum dots are emerging as a cost-effective materials system for both emitting and detecting mid-infrared light. Philippe Guyot-Sionnest’s group at the University of Chicago is working on developing this technology, and their latest paper describes a quantum-dot-based light source that is as efficient as current commercial devices.
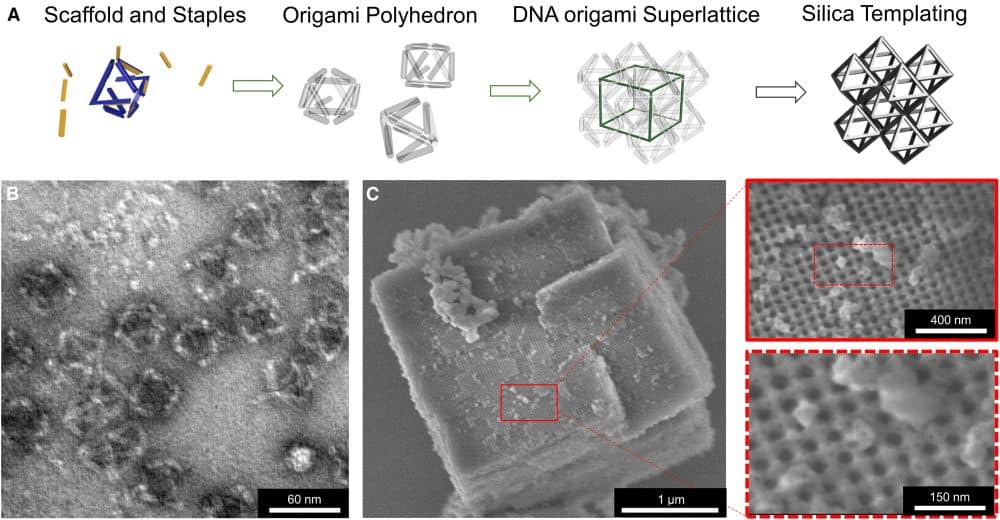
Read MoreIn recent decades, researchers have explored using deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as a scaffold for programmable nanostructures. Now, researchers at Columbia University, the University of Connecticut, and Brookhaven National Laboratory collaborated to show that glass-coated DNA scaffolds have potential as lightweight and high-strength materials.
Read MoreThe increasing use of nanoparticles across all sectors has led to some concerns within the food industry, as nanoparticles do not necessarily behave the same way as their larger counterparts. A new study by Stanford University researchers showed that mesoporous silica, a common food additive, can react with key biomolecules, which could lead to increased oxidative stress in the body.
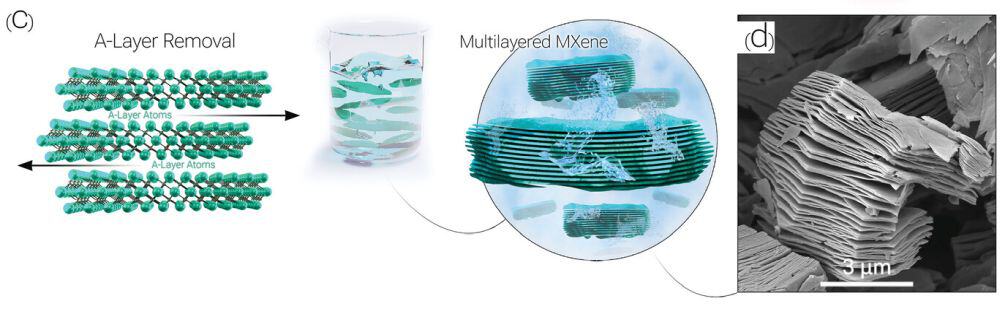
Read MoreDespite the meteoric rise of MXenes from discovery to commercial products in only a decade, the environmental impacts of MXene synthesis have not been assessed systematically. ACerS member Babak Anasori helped lead two recent studies that provided a life cycle assessment and step-by-step guide for synthesizing Ti3C2Tx MXenes, respectively.
Read MoreCurrent methods for controlling “runaway” thermal reactions such as combustion and pyrolysis remain rather rudimentary. Researchers led by North Carolina State University developed a new nanocoating that, when applied to a material before combustion, allows for the reaction rate and direction of ignition propagation to be controlled.
Read MoreGrowing carbon nanotubes on metal foils rather than traditional silicon or quartz substrates would allow the process to be easily integrated into large-scale manufacturing processes. But metal foils present other challenges, such as reactivity at high temperatures. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers published a review paper summarizing efforts to overcome these challenges.
Read MoreFerroelectricity traditionally is believed to only occur in compounds. However, in the past decade, some theoretical works suggested that ferroelectricity is possible in certain elementary substances. Now researchers in China and Singapore experimentally confirmed ferroelectricity in monolayer α-phase bismuth.
Read More