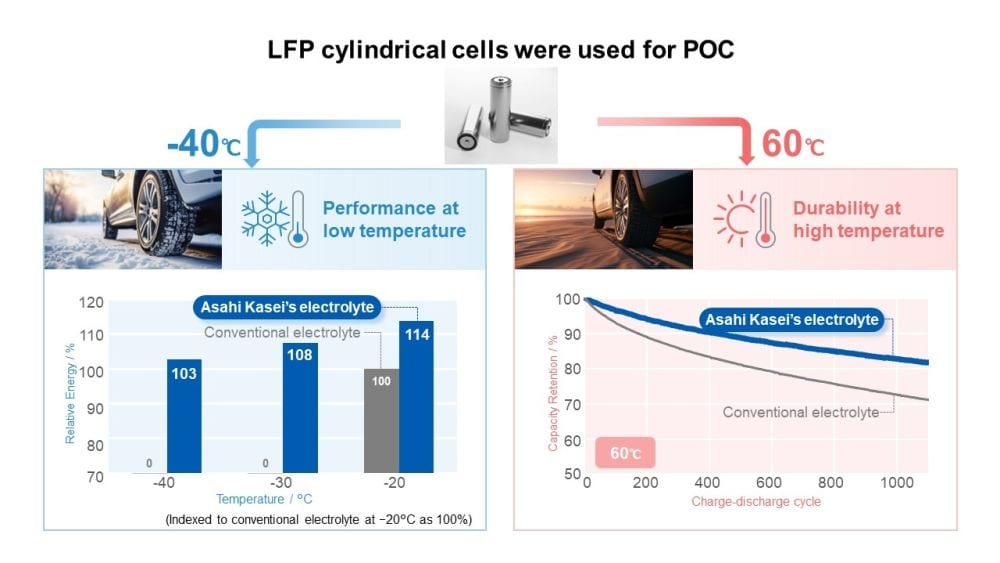
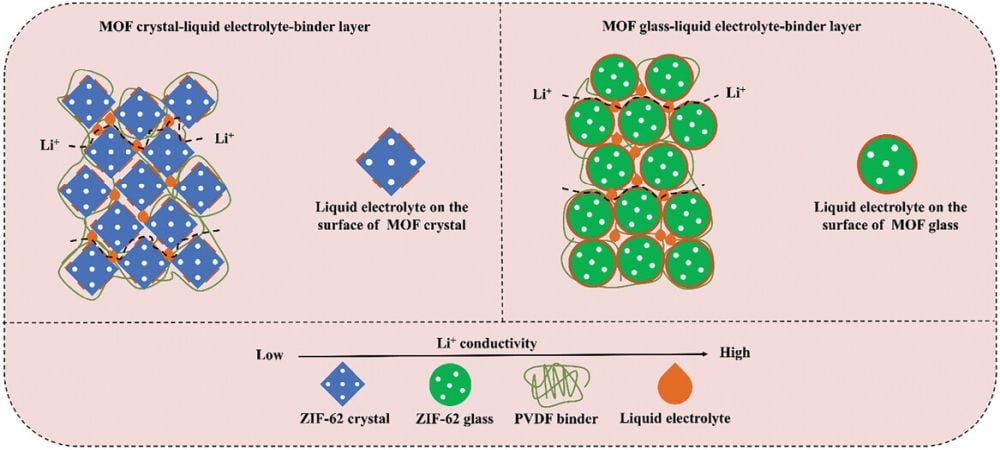
New electrolyte formulas with higher ionic conductivities could help expand the temperature range in which lithium-ion batteries can viably operate. Researchers at Japanese chemical company Asahi Kasei developed a novel acetonitrile-based electrolyte that they plan to commercialize by 2025.
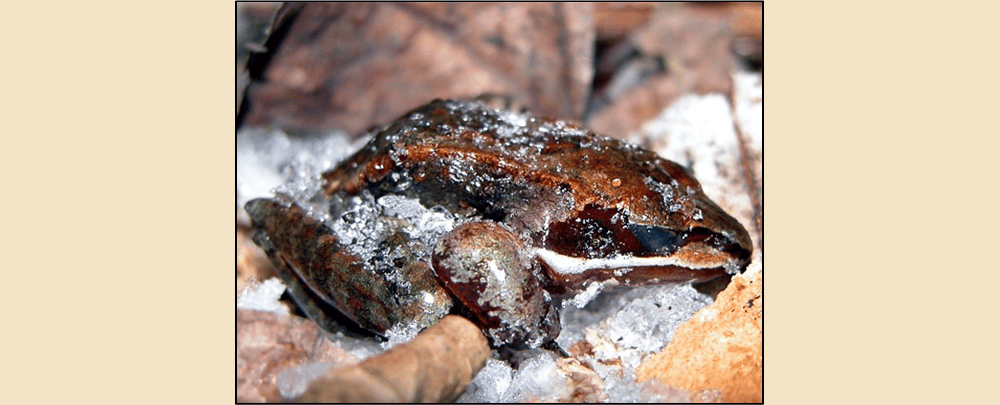
Read MoreWood frogs can freeze and thaw themselves completely unharmed, and this unique ability could help revolutionize the organ transplant industry by inspiring methods for long-term storage of organs.
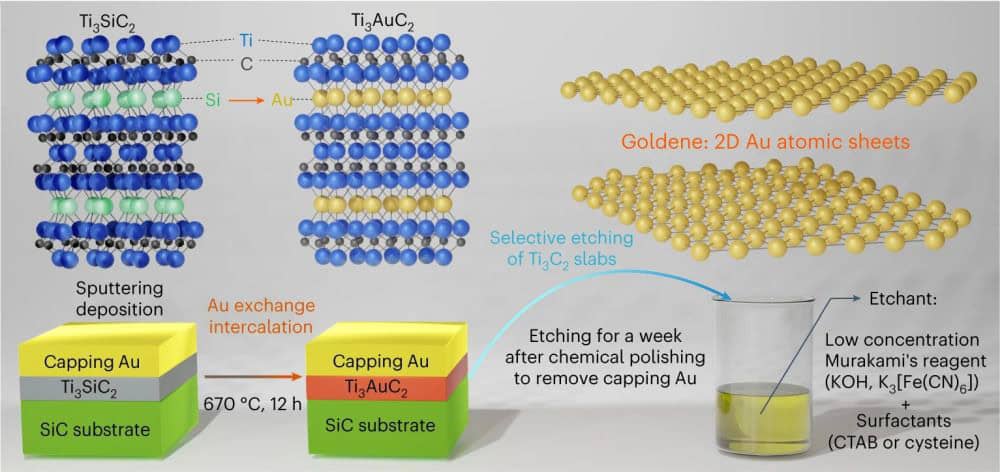
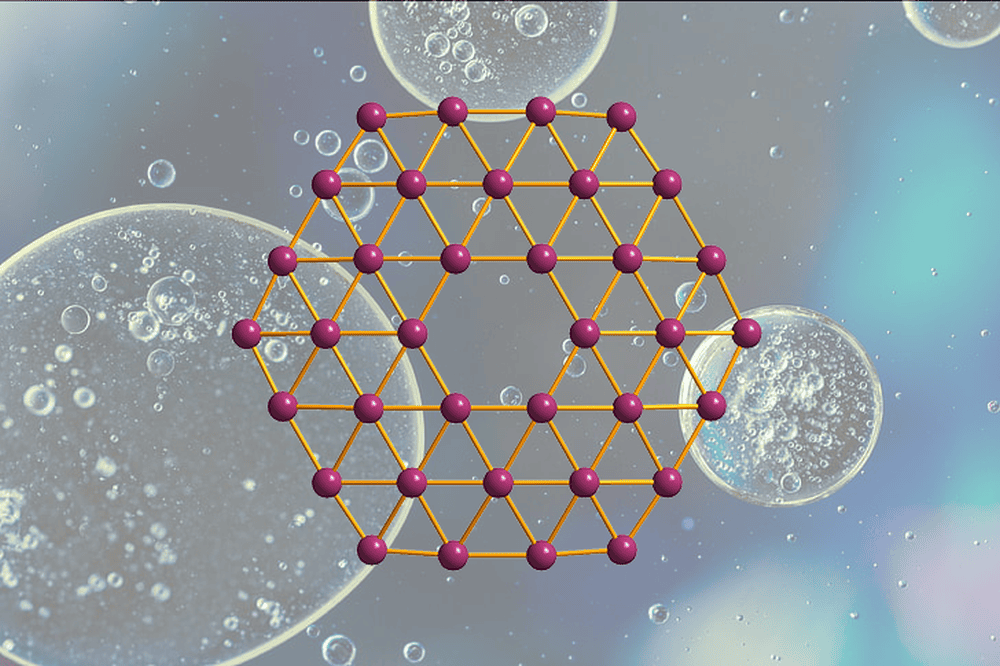
Read MoreIn a breakthrough for 2D materials, researchers at Linköping University in Sweden reported a method for synthesizing freestanding single-atom-thick sheets of gold.
Read MoreDespite great progress in materials synthesis, it remains a standing challenge to fabricate transparent glass composites with high crystallinity. An international group of researchers developed a novel mixed melt synthesis method that allows for the fabrication of such composites using conventionally incompatible materials.
Read MoreIn a new record for auxetic materials, researchers at the University of Western Ontario synthesized 2D flakes of tungsten semicarbide than can expand up to 40% under applied strain.
Read MoreBorophene, a relatively new nanomaterial, is beginning to make its way into biomedical applications. Researchers at The Pennsylvania State University showed that synthesizing borophene with chiral structures allows it to interact with mammalian cells in distinct ways.
Read MorePlastic deformation of polycrystalline ceramics at room temperature is hindered by the lack of sufficient independent slip systems within the material’s structure. Researchers in Germany circumvented this limitation by focusing on deformation in the near-surface region, which demonstrates several useful dislocation mechanisms not available in the bulk region.
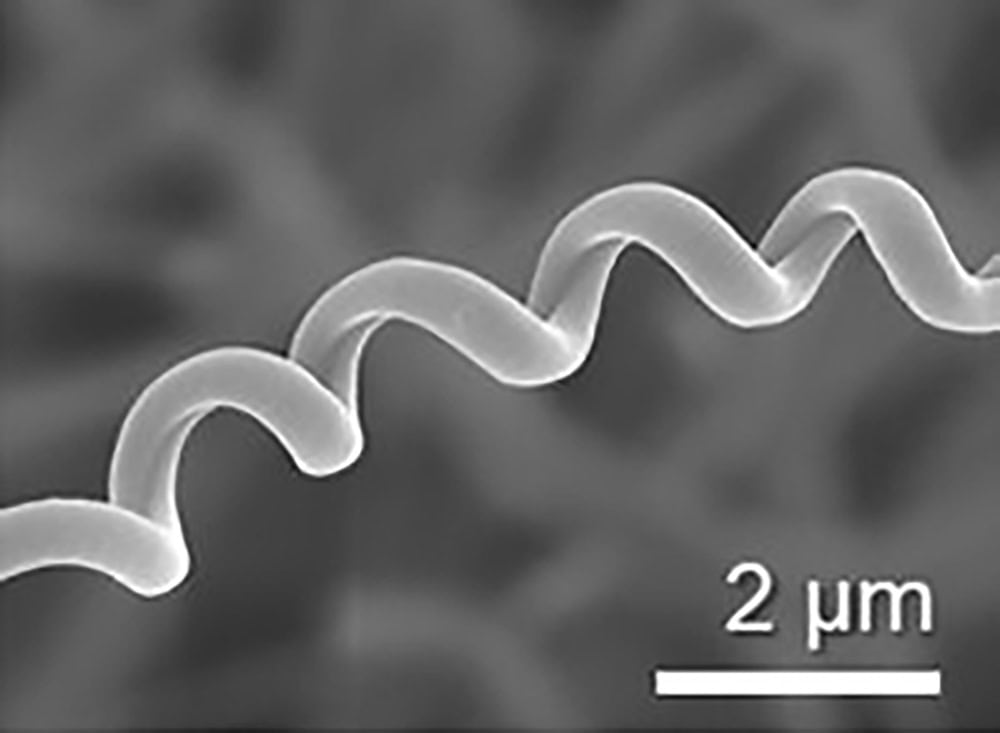
Read MoreConventional electrospinning of sol–gel ceramic solutions places limitations on the composition and structural integrity of the resulting fiber. University of Oxford researchers showed that uniform, flexible ceramic nanofibers and springs can be created using the modified technique of coaxial electrospinning.
Read More