Hexagonal boron nitride has recently emerged as a potential material for hosting qubits, the basic unit of quantum information, on a smaller scale than diamonds, the traditional go-to material for quantum systems. Now, researchers at the University of Technology Sydney in Australia described a way to stabilize charge states in hexagonal boron nitride.
Read MoreThe September 2023 issue of the ACerS Bulletin—featuring an overview of the current gallium nitride-based device market—is now available online. Plus—ACerS Awards of 2023 and C&GM.
Read MoreGroup-III-nitride semiconductors have considerable potential for electronic and optoelectronic applications, but unintended defects tend to form in their structure during fabrication, which may affect the electrical properties. Two researchers at the University of British Columbia detailed the striking contrast between the effects of threading dislocation lines in gallium nitride versus indium nitride.
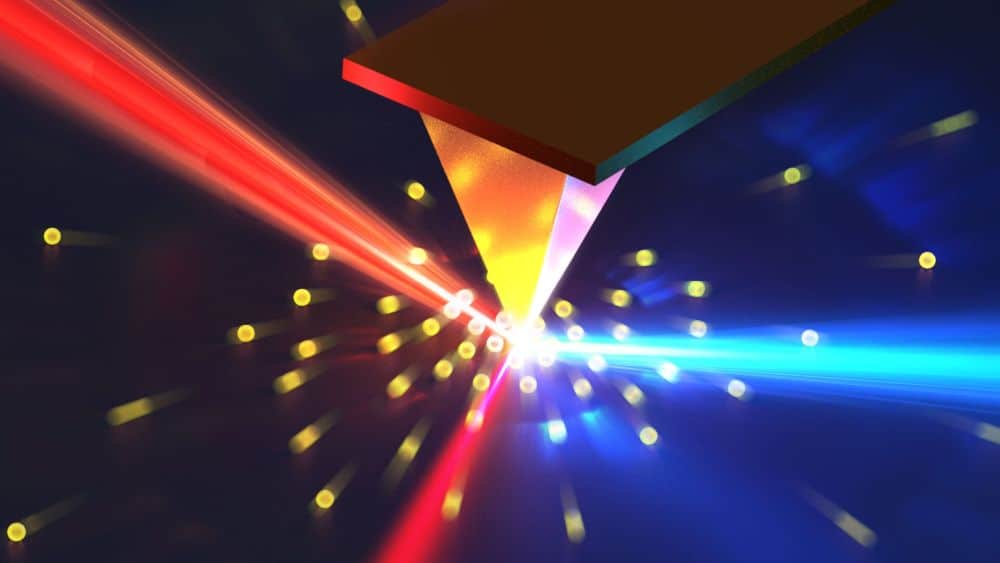
Read MoreTo date, efforts to study carrier dynamics in semiconductor materials have primarily focused on narrow bandgap semiconductors. Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, propose a method that combines ultrafast nanoscale measurements and theoretical modeling to probe carrier behavior in semiconductors with wider bandgaps.
Read MoreFor the first time since 2020, the Electronic Materials and Applications Conference met in person in Orlando, Fla., Jan. 17–20, 2023. Close to 270 attendees from 20 countries attended the three-day conference.
Read MoreAwareness of lead’s toxicity drives research on alternative lead-free piezoelectric materials. But traditional high-temperature sintering processes can inadvertently deteriorate a lead-free ceramic’s piezoelectric response. A two-step sintering process can minimize this deterioration, and researchers in China identified the optimum temperature and dwell time for the first step.
Read MoreFerroelectric materials are expected to revolutionize the next generation of ultralow-power microelectronics. In a recent study, researchers led by the University of California, Berkeley achieved atomic-scale ferroelectricity in fluorite-structured zirconium dioxide thin films on silicon.
Read MoreThe typically brittle nature of ceramics can hamper its formation into complex parts. Northeastern University researchers demonstrated that a highly oriented boron-based ceramic matrix composite can be shaped via thermoforming, which could hold implications for the electronics field.
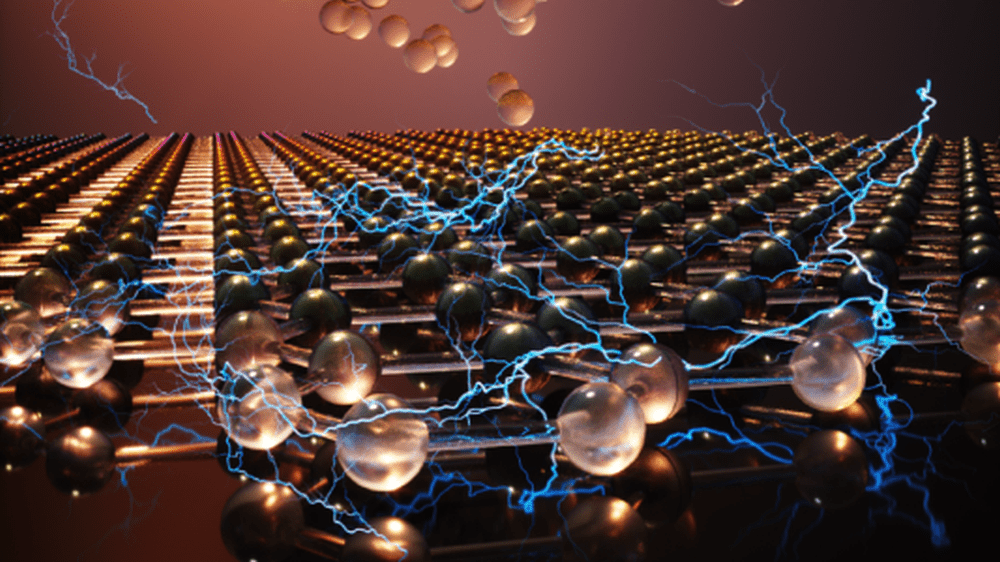
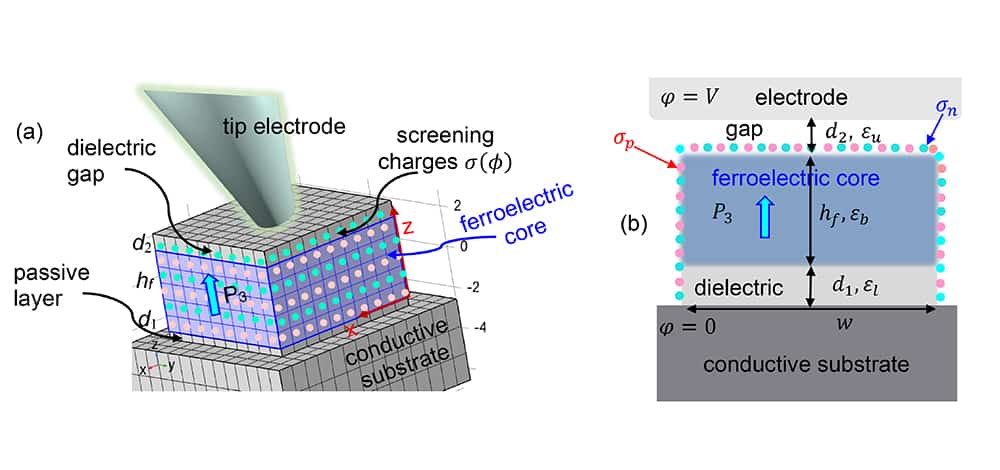
Read MoreThere still is much to learn about how surface-charge dynamics influence the behavior of ferroelectric materials. In a recent open-access paper, researchers from the United States and Ukraine used finite element modeling to map these dynamics for ferroelectric nanoparticle dispersions.
Read MoreIn recent years, conflicts over spectrum usage by private, public, and federal entities have reached a fever pitch. The Federal Communications Commission and the National Telecommunications and Information Administration, as well as House and Senate committees, are considering initiatives and legislation to reform and improve spectrum management.
Read More