Exploratory synthesis of nitride materials can be a time-consuming and risky venture. A new map of ternary metal nitrides gives scientists a good idea of where to look for new nitrides.
Read MorePreviously, two separate theories described heat transport in ordered and disordered materials. A new general theory by Swiss and Italian researchers describes thermal transport in both, as well as everything in between.
Read MoreRecent research may enable integration of boron nitride into next-gen electronics. Researchers have proven boron nitride’s high thermal conductivity and integrated the material into a flexible yet efficient nanocomposite.
Read MoreResearchers from Nankai and Rice universities found their 3D cross-linked graphene foam could retain its reversible and robust compressive elasticity at temperatures near absolute zero, a property not observed previously for any other bulk material.
Read MoreResearchers at MIT developed a robot that can effectively separate mixed recyclable materials, using two flexible silicone “hands” to feel the difference between paper, metal, and plastic.
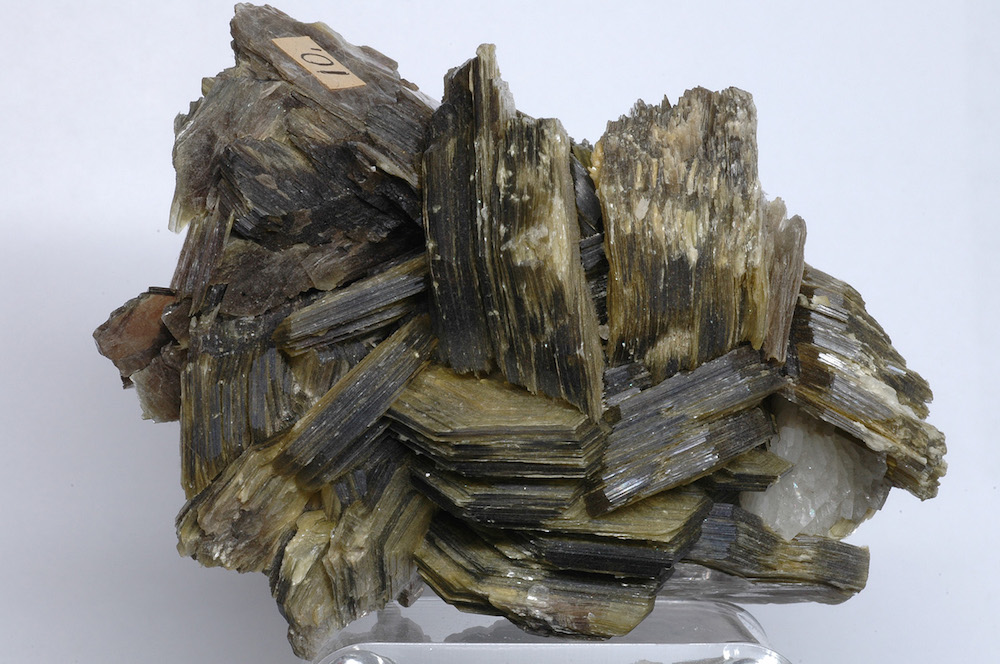
Read MoreJapanese researchers found they could explain macroscopic friction in muscovite using theoretical calculations of microscale frictional forces. They hope to develop a theory that can explain frictional strength across a broad range of clay and clay-like minerals.
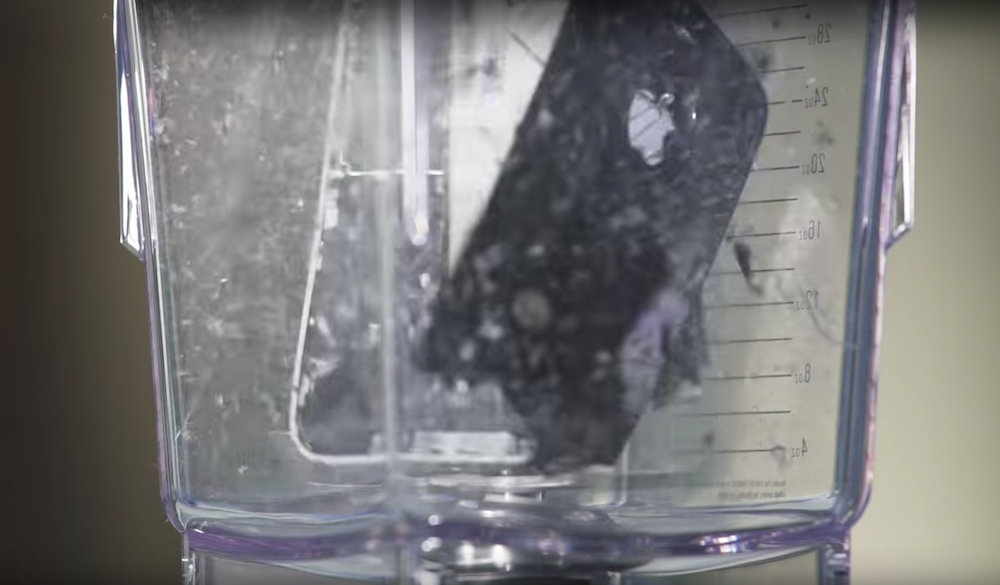
Read MoreUniversity of Plymouth researchers put a smartphone in a blender to quantify the materials composition of an average phone. They hope to encourage greater recycling rates with their project.
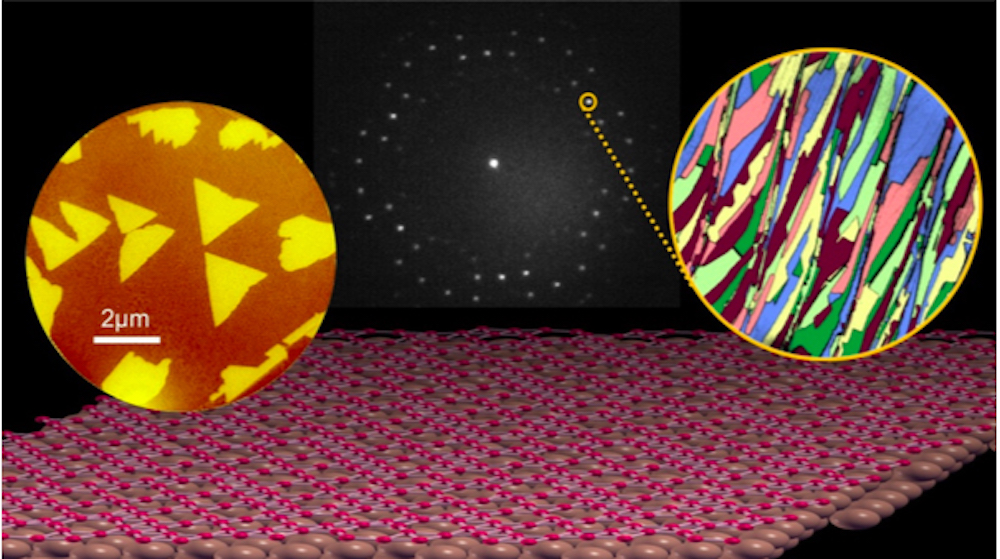
Read MoreBorophene, a 2D sheet of boron atoms, is extremely flexible, strong, and lightweight—even more so than graphene, its carbon-based cousin. Researchers at Brookhaven National Laboratory and Yale University have succeeded in growing large-area sheets of borophene for the first time.
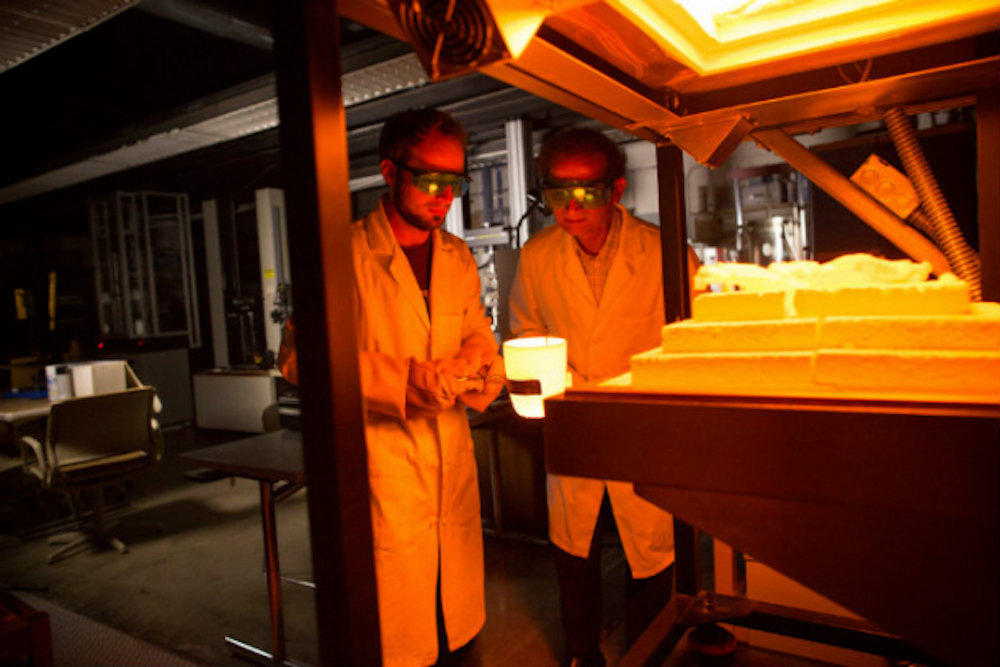
Read MoreResearchers from Lehigh University and Corning Inc. showed the temperature of electrically heated glass defies predictions of traditional Joule’s first law by a long shot—over a thousand degrees! However, the law still appears to work when microscale heterogeneities are given due consideration.
Read More